Introduction
Rodents belong to the class of mammals and are one of the most abundant mammal groups, accounting for more than 40% of the total number of mammals. They are widely distributed geographically, almost all over the world except Antarctica, and are distributed all over the world with great diversity in morphology, behavior and lifestyle. The Rodent Genome, Microbiome, and Pathogen Atlas is a platform for large-scale comprehensive annotation and in-depth analysis of rodent species reference genome, microbiome and pathogen data, including the development of genome browser, functional gene annotation, comparative genome analysis and compilation of rodent zoonotic pathogens. To date, the Rodent Genome and Pathogen Atlas has collected 121 species reference genomes from 29 families and 78 genera, as well as 1,143 viromes from 14 countries and 2,923 16S rRNA gene amplicons.And 21,852 records of pathogen sequences that reported in rodents from NCBI GenBank database and the European Nucleotide Archive database of the EMBL-EBI. In addition, the database provides functions such as species comparative genome analysis, rodent zoonotic pathogen catalog, data visualization, blast comparison, primer design and online analysis, which provide convenience and available resources for the study of genomic genetic evolution of different rodent species.
How to use RGPMdb
1. Basic biological information module of rodent species
This module contains the basic biological information of 2706 rodent species, including a series of basic biological information available to rodents, such as species feature pictures, species scientific and generic names, species taxonomic levels, species global geographical distribution, species sea wave distribution and habitat types. For rodent species with genomes, virome, amplicon, and natural infectious agents, all data are presented in an integrated display to facilitate browsing of the species omics information and detailed pathogen carrying status.


2. Rodent species genome browser and comparative genome analysis
In this study, a genome browser based on Jbrowser2 was developed in the database genome module, and detailed gene annotation information of rodent species was integrated, including the description of external biological function annotation database of genes and link acquisition. Through genome browser, users can quickly browse any genome region and gene sequence of interest, and it is easy to view the relevant gene biological function annotation content and extract the corresponding sequence, which realizes the convenient visualization of complex genomic information.
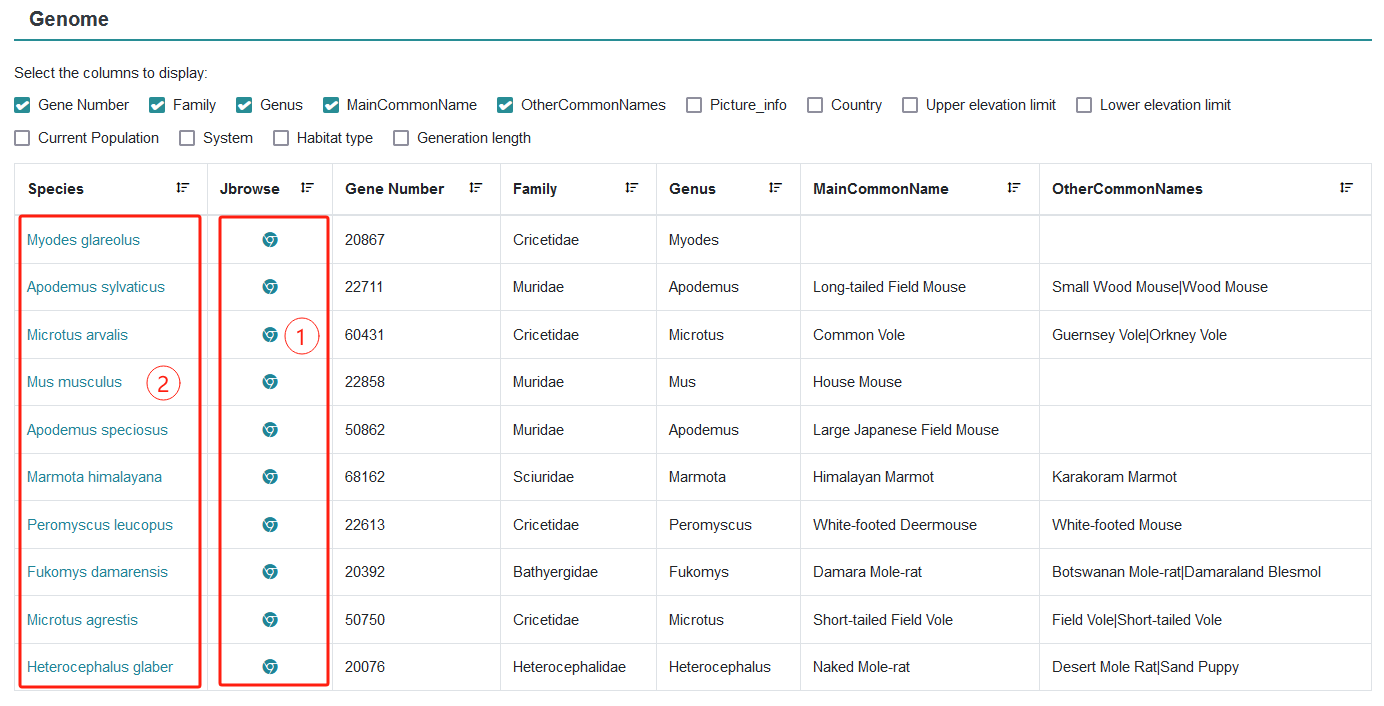
Step 1: Click on the species name to link to the Click on the species name to link to the Taxonomy module.
Step 2: Click on the Jbrowse links to view the specific rodent genome browser module, loading multiple tracks, which can be shown or hidden by checking "On" or "off" in the left column, and information about protein-coding genes.
3. Gene search and gene annotation
Detailed gene annotation information of species can be obtained by searching gene id or location of genome interval for precise matching, or searching keywords in annotation description for fuzzy matching. In order to comprehensively annotate all protein-coding genes in 121 rodents, we built a "Gene annotation" module, which compiled and integrated functional annotation information from six major databases: NR, Swiss-Prot, KEGG, GO, COG, and Pfam.
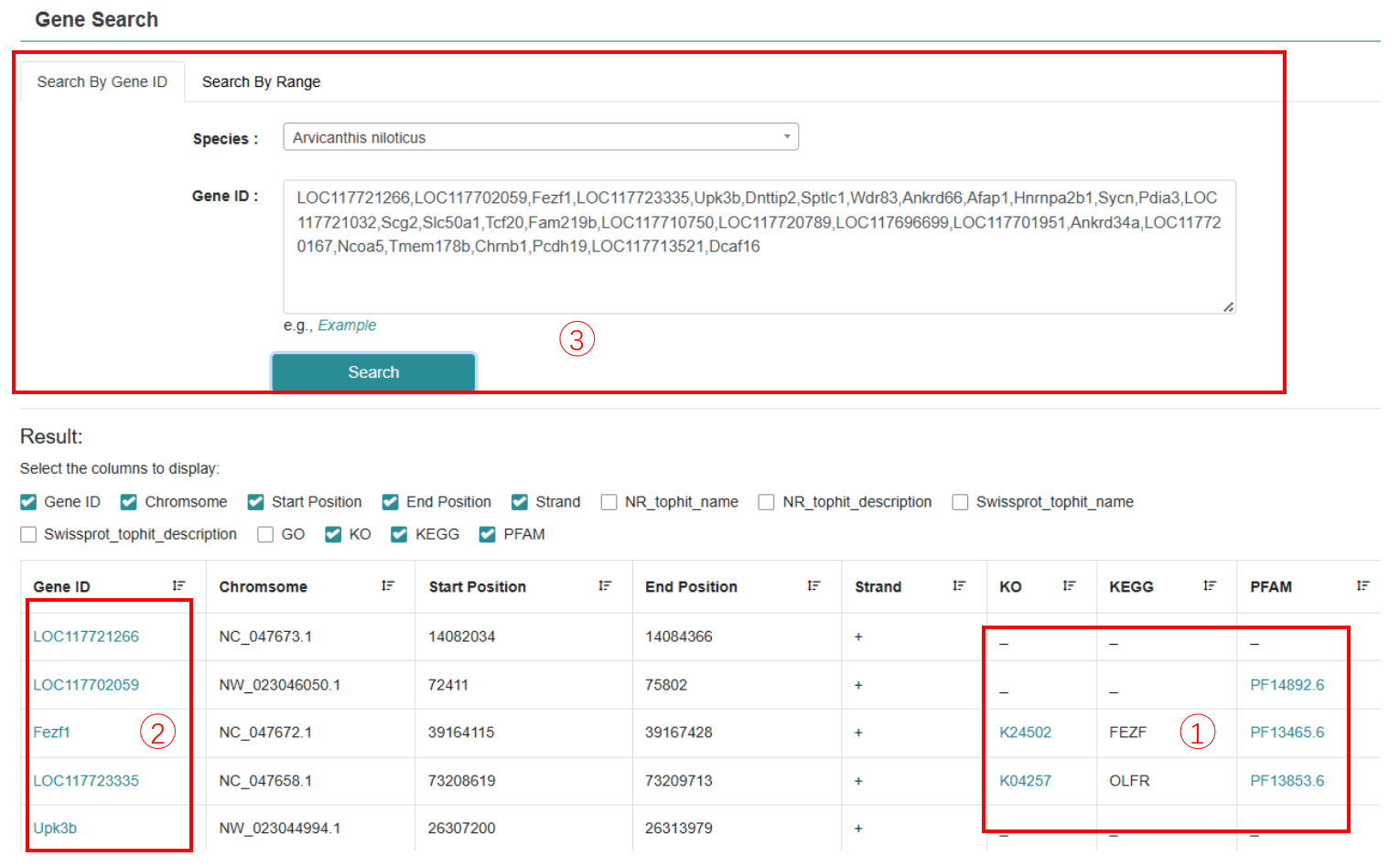
Step 1: Choose rodent species and gene ID.
Step 2: Choose a search option to obtain basic gene information about gene size and gene location.
Step 3: Get the function annotation result. Click on the gene ID to browse the basic information of the gene and view the functional annotation information of the corresponding gene.
4. Genome Synteny analysis
In order to understand the process of genome evolution among rodent species, this study conducted a collinearity analysis of 465 genome pairs of 31 rodent species with high quality chromosome level, and the obtained collinear block gene results were integrated into the "Synteny" module of the database. In this module, users can view and compare the level of conservation between 31 rodent genomes based on different reference genomes, or select specific species of concern through the species option, and study the synergies of detailed species chromosome genomes in a zoomed-in view. In addition, the database provides download options for users to obtain macrocolinear collinear visualizations, homologous gene pairs and related gene sequences.
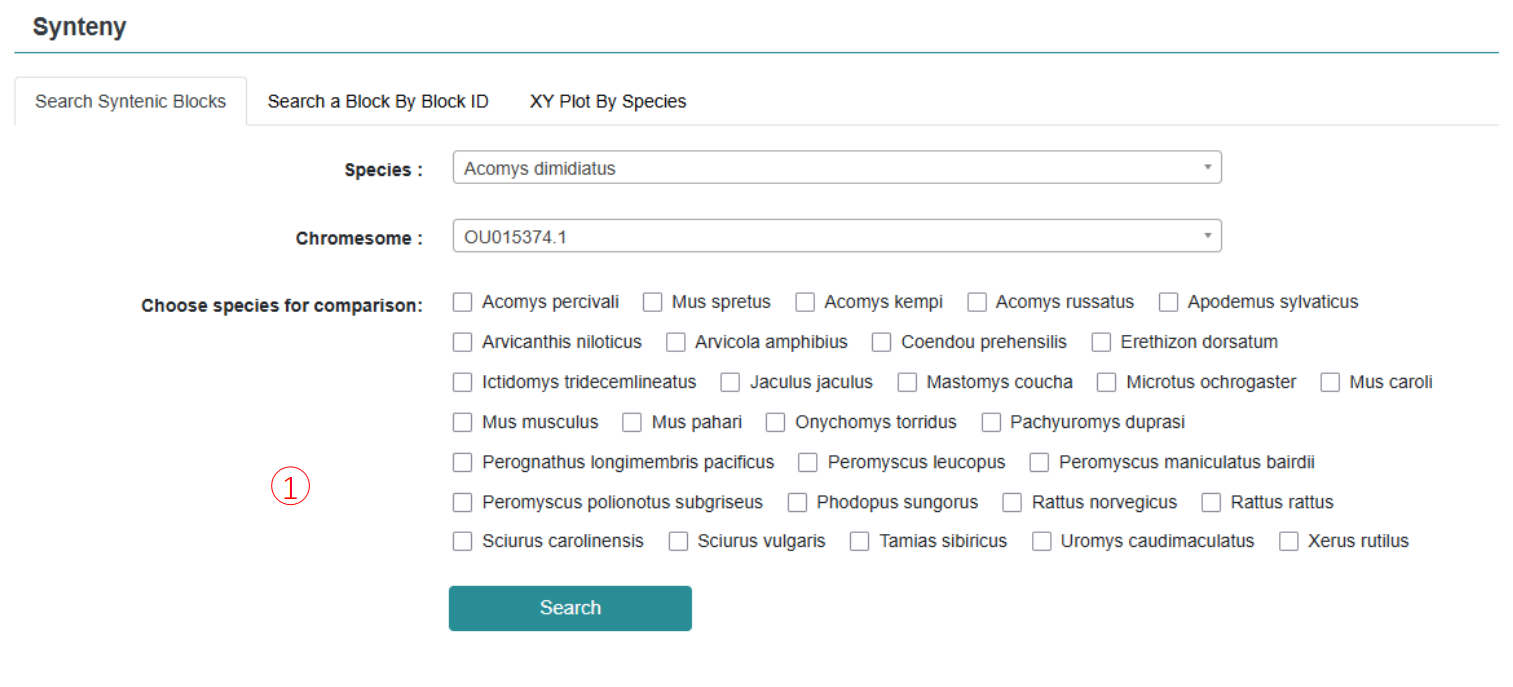
Step 1: Choose species and chromosome number and multiple species can be selected for collinear comparison.
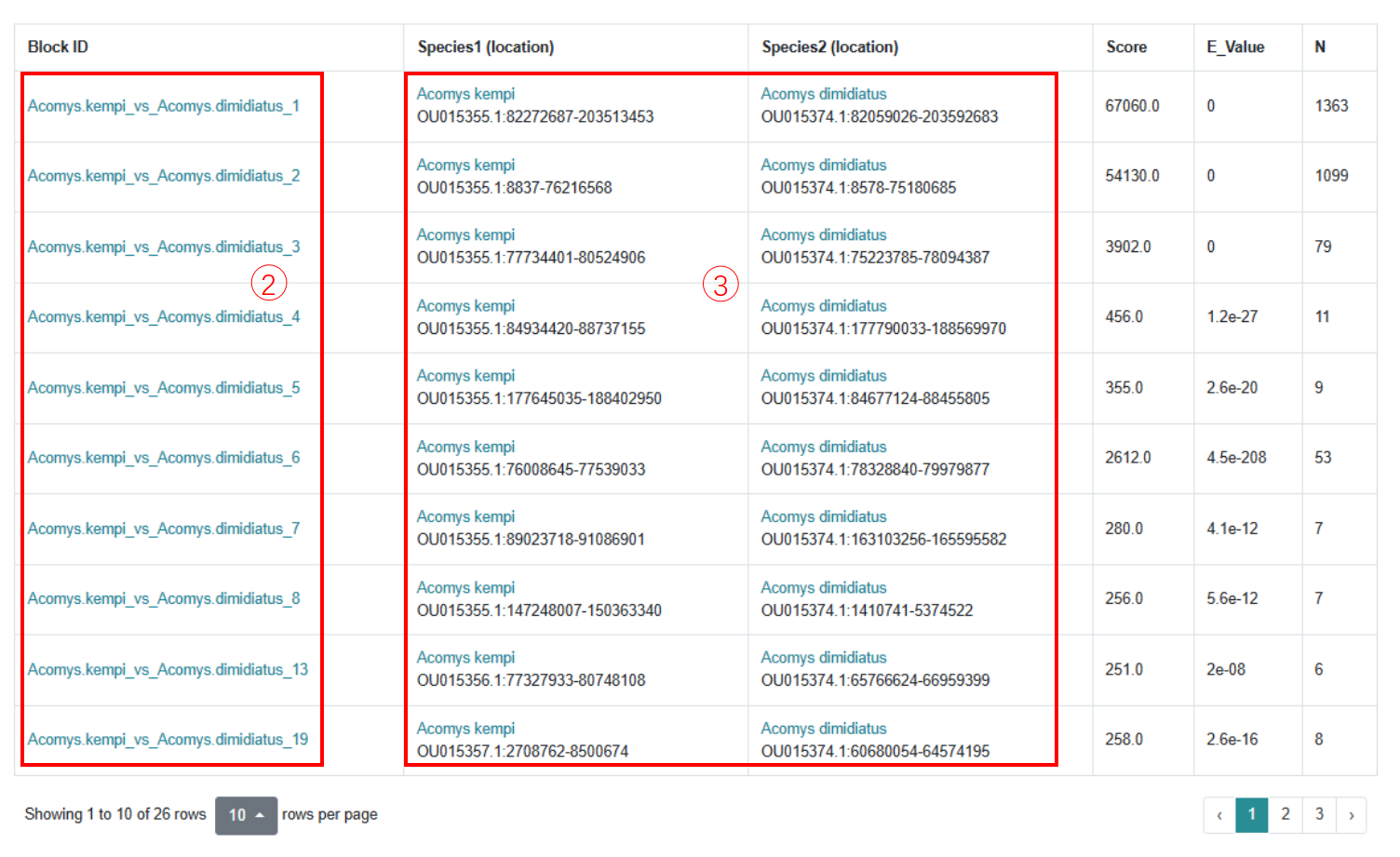
Step 2: Click on the species matching relationship to get the results of comparison of genomic homologous blocks between two species.
Step 3: Detailed location relationships of homologous blocks on the genome, and click on the species name to view the species biological information and omics data.
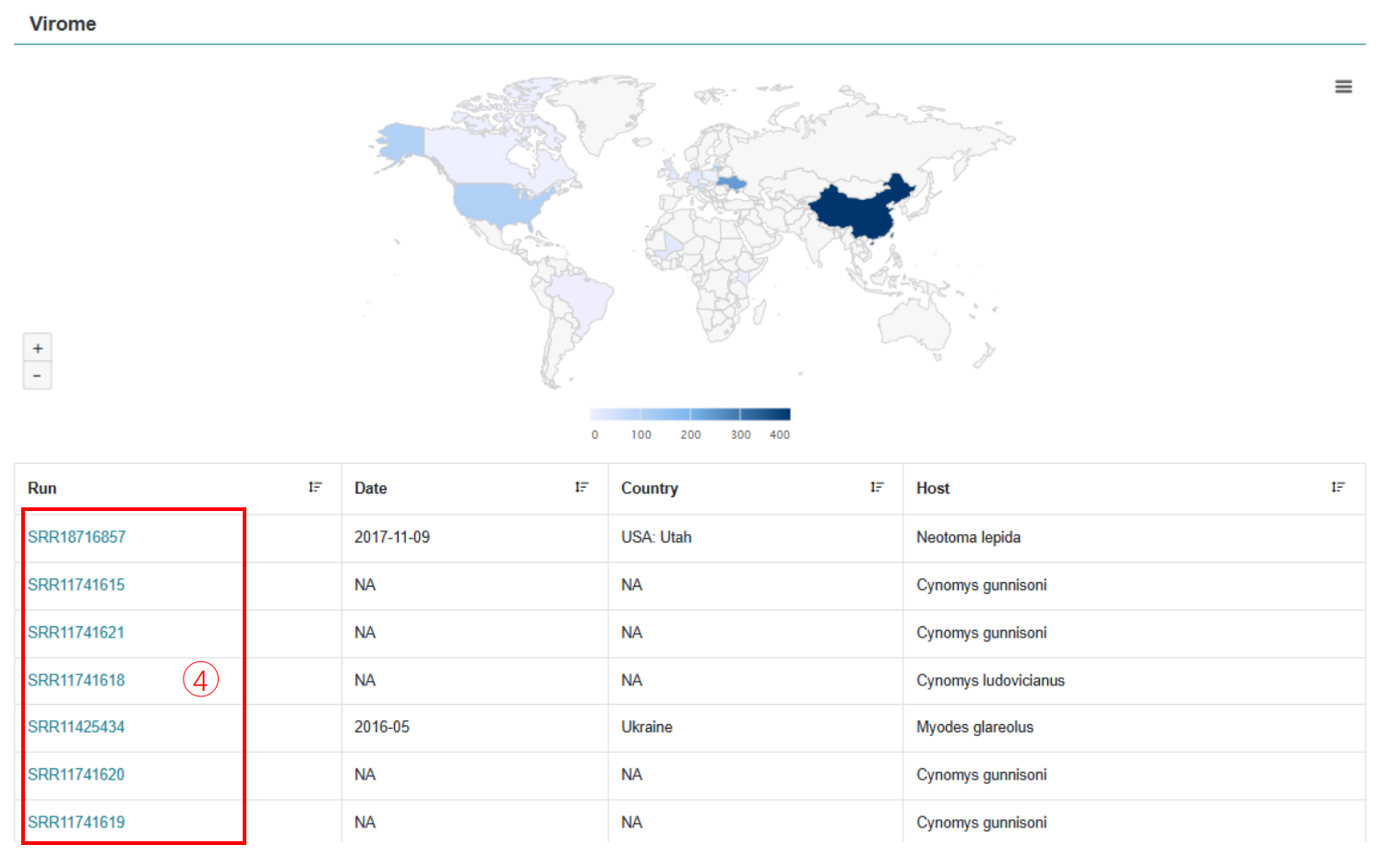
5. Virome
Click on the SRA data accession number to view reliable annotated results for each wild rodent sample virome.
6. Blast
Blast-based sequence search and comparison of your supplied sequence data.
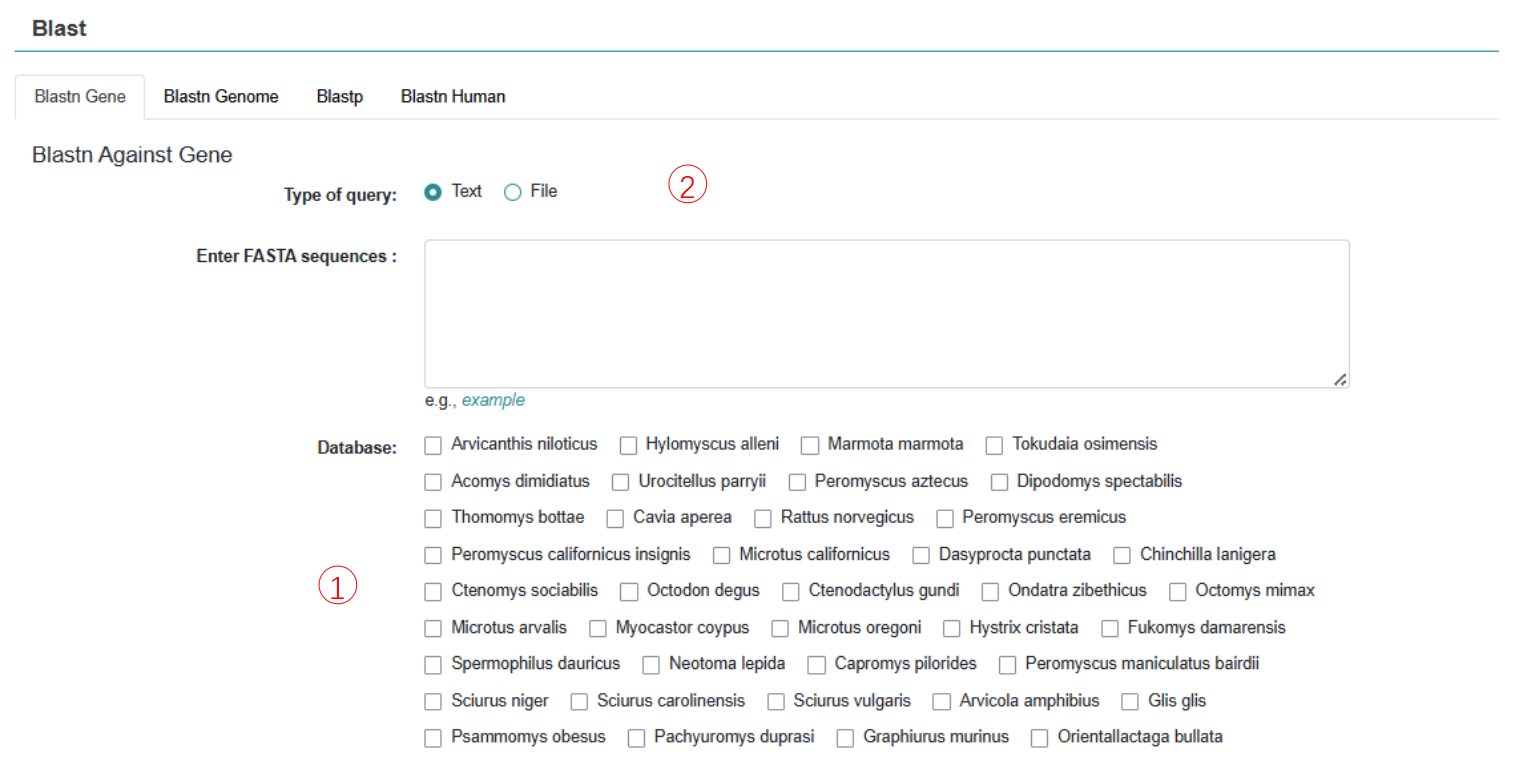
Step 1: Enter a sequence or file in FASTA format.
Step 2: Select the database to blast.

Step 3: Set E-value threshold and max target sequences.
7. Tools
The database provides a series of auxiliary biological experimental research tools such as sequence alignment, primer design, sequence extraction and gene enrichment analysis.

Step 1: The user selects the tool they want to use and clicks on the corresponding name.
Step 2: Follow the instructions for each tool.
